The purpose of the project is to understand the relation between the chemical structure of the bent-shaped molecule and the physical properties of the NTB phase. The activities include design and synthesize of new bent-shaped compounds, which present the NTB phase and investigation of their macroscopic properties.
Results:
During the study of novel bent-shaped dimers in which naphthyl group has been incorporated into the mesogenic cores, a new liquid-crystalline phase was observed. The very short temperature range (2 K) of the monotropic phase precluded any X-ray or electro-optical investigation on the pure compound and the phase is assigned as Mx. A preliminary electro-optical investigation on the mixture showed that the new phase exhibits a nematic-like response in the electric field.
During the study of novel bent-shaped dimers in which naphthyl group has been incorporated into the mesogenic cores, a new liquid-crystalline phase was observed. The very short temperature range (2 K) of the monotropic phase precluded any X-ray or electro-optical investigation on the pure compound and the phase is assigned as Mx. A preliminary electro-optical investigation on the mixture showed that the new phase exhibits a nematic-like response in the electric field.
Investigation of electric-field effects in the twist-bend nematic phase showed that, due to the periodic NTB structure, the electro-optic effects are not nematic-like but are close analogues to those in the smectic and cholesteric phases. It was demonstrated that, due to the smectic-like macroscopic elasticity of the twist-bend nematic, most of the dielectrically-induced texture transitions, which are typically used in applications of classical nematics, are not of practical interest in the NTB phase because of their long response times and poor reversibility. This is not the case for the fast (sub-microsecond) flexoelectrically-induced rotation of the optic axis, which can find applications for light beam manipulation for instrumentation and telecommunication devices.
- G. Damême, C. Meyer, I. Dokli, A. Lesac, K. Antonova, P. Davidson, I. Dozov, ˝Détermination des constantes élastiques K11 et K33 dans la phase nématique d’un composé possédant une phase nématique twist-bend˝, Division Chimie Physique (DCPhys), Congrès général SFP 2017, Orsay (3-7 srpnja 2017).
- A. Aouini, A. Lesac, C. Blanc, I. Dokli, M. Nobili, ˝Nematic Twist-bend Textures under different anchoring conditions˝, CFCL, ENS Lyon (12-15 rujan 2017).
- 27th International Liquid Crystal Conference (ILCC2018), Kyoto, Japan, 22-27. 07. 2018
- Dozov, I.; Davidson, P.; Luckhurst, G. R.; Dokli, I.; Knezevic, A.; Lesac, A.; Meyer, M.: Temperature Dependence of the Birefringence and the Electroclinic Effect in the Twist-Bend Nematic Phase
- Meyer, C.; Damême, G.; Dokli, I.; Knezević, A.; Lesac, A.; Antonova, K.; Stoenescu, D; Davidson, P.; Dozov, I.:Homeotropic alignment of mesogenic dimers in the nematic and twist-bend nematic phases
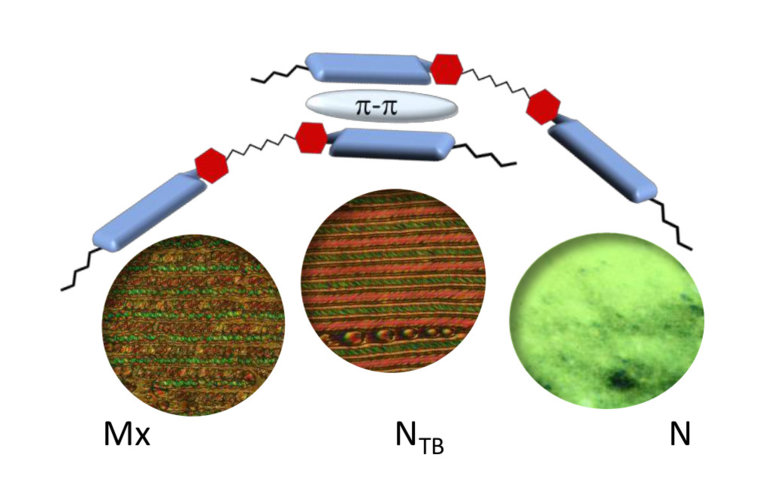
- A. Lesac, A. Knežević, M. Sapunar, A. Buljan, I. Dokli, The Effect of π–π Interactions on Stability of the NTB phase.
- Claire Meyer, Ivan Dozov, Patrick Davidson, Geoffrey R. Luckhurst, Irena Dokli, Anamarija Knezevic, Andreja Lesac, "Electric-field effects in the twist-bend nematic phase", Proc. SPIE 10555, Emerging Liquid Crystal Technologies XIII, 105550Z (8 February 2018); doi: 10.1117/12.2301296
- A. Knežević, M. Sapunar, A. Buljan, I. Dokli, Z. Hameršak, D. Kontrec, A. Lesac*, "Fine-tuning effect of π–π interactions on the stability of the NTB phase" Soft Matter 14 (2018) 8466-8474, DOI: 10.1039/c8sm01569d.